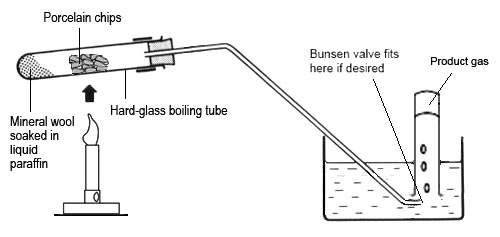
1- Heat the hydrocarbon (e.g. paraffin).
2- After a few seconds, move the Bunsen burner to heat the silica/aluminium catalyst
3- Alternate between the two until the paraffin vaporises and the catalyst glows red
4- The heated paraffin vapour cracks as it passes over the heated catalyst
5- small alkanes collect at the end of the boiling tube, while alkene gases travel down the delivery tube
6- The alkenes are collected through water using a glass jar
In industry, vapourised hydrocarbons are passed over a powdered catalyst at about 600-700°C. silica and aluminium are used as catalysts.
Notes credit: CGP
No comments:
Post a Comment